Table of Contents
查看 linux 版本
方法一
$ cat /etc/issue
Debian GNU/Linux 9 \n \l
方法二
$cat /etc/issue.net
Debian GNU/Linux 9
方法三
$ uname -a
Linux 1de774242804 4.9.125-linuxkit #1 SMP Fri Sep 7 08:20:28 UTC 2018 x86_64 GNU/Linux
方法四
$ cat /proc/version
Linux version 4.9.125-linuxkit (root@659b6d51c354) (gcc version 6.4.0 (Alpine 6.4.0) ) #1 SMP Fri Sep 7 08:20:28 UTC 2018
方法五(Mac 和 Ubuntu/centos 测试可行)
$ echo $OSTYPE
darwin18.0
$ echo $OSTYPE
linux-gnu
$ echo $OSTYPE
linux-gnu
查看使用的 shell
方法一:查看\$SHELL 环境变量
shiming@pro ➜ ~ echo $SHELL
/bin/zsh
方法二:echo \$0, 据说不是对所有 shell 都支持
shiming@pro ➜ ~ echo $0
-zsh
方法三:敲一个不存在的命令,查看提示
shiming@pro ➜ ~ tom
zsh: command not found: tom
查看系统支持的 shell
root@sz ➜ ~ cat /etc/shells
# /etc/shells: valid login shells
/bin/sh
/bin/dash
/bin/bash
/bin/rbash
/bin/zsh
/usr/bin/zsh
/usr/bin/tmux
查看系统信息
使用uname命令可以查看系统信息,了解系统信息对安装软件很有帮助,安装软件时必须知道是装 32 位还是 64 位,是 x86 架构还是 i686 架构,诸如此类。
mac 示例
shiming@pro ➜ ~ uname -a
Darwin pro 18.2.0 Darwin Kernel Version 18.2.0: Fri Oct 5 19:41:49 PDT 2018; root:xnu-4903.221.2~2/RELEASE_X86_64 x86_64
ubuntu 示例
root@MNG-BC ➜ ~ uname -a
Linux MNG-BC 4.4.0-142-generic #168-Ubuntu SMP Wed Jan 16 21:00:45 UTC 2019 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
查看硬件信息
lshw命令可以查看硬件信息
lscpu命令可以查看 cpu 信息
root@MNG-BC ➜ ~ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 12
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-11
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 6
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 85
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8163 CPU @ 2.50GHz
Stepping: 4
CPU MHz: 2499.998
BogoMIPS: 4999.99
Hypervisor vendor: KVM
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 1024K
L3 cache: 33792K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-11
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ibrs ibpb stibp kaiser fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm mpx avx512f rdseed adx smap avx512cd xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1
cat /proc/cupinfo可以查看 cpu 信息,每一个核心都会列出来,以core id区分
root@MNG-BC ➜ ~ cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 85
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8163 CPU @ 2.50GHz
stepping : 4
microcode : 0x1
cpu MHz : 2499.998
cache size : 33792 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 12
core id : 0
cpu cores : 6
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ibrs ibpb stibp kaiser fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm mpx avx512f rdseed adx smap avx512cd xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1
bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf
bogomips : 4999.99
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
系统时间 – date
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ date #打印系统时间
2018年 07月 25日 星期三 19:38:53 CST
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ date +%x #打印日期
2018年07月25日
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ date --utc #打印UTCtime
2018年 07月 25日 星期三 11:55:17 UTC
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ date +%T #打印hh:mm:ss time
19:56:57
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ date +%s #打印unix时间戳,精确到秒
1532519829
本地化设置
locale命令
locale – description of multilanguage support
A locale is a set of language and cultural rules.
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/locale.7.html
系统语言 – LANG
修改系统语言
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ cat /etc/locale.conf #查看linux系统语言设置
LANG=en_US.UTF-8 #修改语言只需修改这行
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ echo $LANG #查看ssh语言环境变量设置
zh_CN.UTF-8 #系统为英文,但ssh设置为中文,所以通过ssh远程连接还是会显示中文
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ LANG=en_US.UTF-8 #通过给LANG赋值改变ssh语言(这样只是临时修改,下次ssh登录时还是会显示中文)
使用本机或服务器语言
mac 为例,在本机中 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config,如果希望在 ssh 连接中传入 loacle 环境变量,则放开注释,否则用#号注释以下行(使用服务器的系统语言)
SendEnv LANG LC_*
主机名 – hostnamectl
redhat 中有三种主机名类型:–pretty, –static, and –transient, 参考 1 and 参考 2
| Hostname Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Static | Assigned by the system admin |
| Transient/Dynamic | Assigned by DHCP or mDNS server at runtime |
| Pretty | Assigned by the system admin. Its can be used as Description like “Oracle DB server” |
查看和修改主机名
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ hostnamectl #查看所有主机名
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ hostnamectl set-hostname redhat #修改主机名(三个主机名都改为redhat)
[shiming@redhat ~]$ #修改后重启,主机名变了
注意:/etc/hosts文件中映射的 hostname 要自己手动修改
修改主机名(临时修改)
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ hostname #查看主机名
red-hat-enterprise-linux.shared
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ hostname redhat #修改主机名为redhat
hostname: you must be root to change the host name #要root权限才能修改
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ sudo hostname redhat #使用管理员权限修改
[sudo] password for shiming:
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ hostname #查看修改后的主机名
redhat
#重启主机名不变
命令行技巧
移动
在敲击命令行时,可以用到以下快捷键提高效率
ctrl + a 移到行首
ctrl + e 移到行尾
meta + f 向前移一个 word
mtea + b 向后移一个 word
Ctrl + b 后移一个字符
Ctrl + f 前移一个字符
Ctrl + d 删除当前字符
Backspace 删除前一个字符
Ctrl + – 撤销
ctrl + l 清屏
mata 键在 windows 就是 alt 键,mac osx 用户需要手动开,根据约定,meta 键是专门用来处理单个词(word)的。
剪切和粘贴
ctrl + k 从光标剪切到行尾
ctrl + y 粘贴
搜索命令行历史
ctrl + r 敲入搜索关键字搜索
继续按 ctrl + r 搜索结果列表
ctrl + j 选定当前命令
ctrl + g 取消搜索
搜索命令
whatis命令会精确搜索 whatis 数据库,给出命令的简介
shiming@pro ➜ ~ whatis cal
cal(1), ncal(1) - displays a calendar and the date of Easter
apropos是whatis的模糊搜索版,会全文模糊搜索 whatis 数据库
shiming@pro ➜ ~ apropos cal
sudo 运行上一个命令
!!是上一个命令的别名,所以sudo !!可以以管理员权限执行上一个命令
sudo !!
sudo 执行一个长命令
sudo 有时在执行一个长命令时 sudo cat /dev/null > /var/log/dpkg.log 还是会提示权限不够,因为 sudo 只能让 cat 命令以 root 的权限执行,而对于 > 这个符号并没有 root 的权限。
这时要用 sh -c 将整个长命令一起执行,全部提升到 root 权限执行。
sudo sh -c "cat /dev/null > /var/log/dpkg.log"
文件类型 – file
Linux 不以文件名后缀来识别文件类型,通过 file 命令可以查看文件类型,一般文件类型分为 3 类
| keyword | description |
|---|---|
| text | 可读文本 |
| executable | 可执行文件 |
| data | 除此之外的叫做 data,一般是二进制的或不可打印的 |
[shiming@redhat ~]$ file /etc/passwd
/etc/passwd: ASCII text
[shiming@redhat ~]$ file /bin/passwd
/bin/passwd: setuid ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=0a16a7915f7f9b01d96442755257e22067ce5b2c, stripped
文件统计 – wc
wc for word count, print newline, word, and byte counts for each file
[shiming@redhat ~]$ wc /etc/passwd
46 100 2426 /etc/passwd #行数,word数,byte数,文件名
[shiming@redhat ~]$ wc -l /etc/passwd #只打印行数
46 /etc/passwd
磁盘使用情况
df显示磁盘使用情况,默认大小为 bytes,加上-h参数使用更适于人类阅读的方式展示
root@mix2 ➜ bitcoin df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
udev 16G 0 16G 0% /dev
tmpfs 3.2G 4.6M 3.2G 1% /run
/dev/vda1 99G 45G 49G 48% /
tmpfs 16G 40K 16G 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
tmpfs 16G 0 16G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/vdc 1008G 63G 895G 7% /mnt/ethereum
/dev/vdb 1008G 273G 684G 29% /mnt/bitcoin
tmpfs 3.2G 0 3.2G 0% /run/user/0
tmpfs 3.2G 0 3.2G 0% /run/user/1002
文件大小
du命令查看文件大小, du -h, h means human readable,默认
root@mix2 ➜ bitcoin du --max-depth=0 -h
273G .
root@mix2 ➜ bitcoin du --max-depth=1 -h
26G ./testnet3
26G ./omni
223G ./mainnet
273G .
文件打印
开头 – head
默认打印开头 10 行
[shiming@redhat ~]$ head /etc/passwd #头10行
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
可指定打印行数 – head -n [linenum]
[shiming@redhat ~]$ head -n 5 /etc/passwd #头5行
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
末尾 – tail
默认打印末尾 10 行
[shiming@redhat ~]$ tail /etc/passwd
nfsnobody:x:65534:65534:Anonymous NFS User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin
pcp:x:990:985:Performance Co-Pilot:/var/lib/pcp:/sbin/nologin
gnome-initial-setup:x:989:984::/run/gnome-initial-setup/:/sbin/nologin
nslcd:x:65:55:LDAP Client User:/:/sbin/nologin
avahi:x:70:70:Avahi mDNS/DNS-SD Stack:/var/run/avahi-daemon:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
oprofile:x:16:16:Special user account to be used by OProfile:/var/lib/oprofile:/sbin/nologin
tcpdump:x:72:72::/:/sbin/nologin
shiming:x:1000:1000:Shiming Liu:/home/shiming:/bin/bash
指定打印行数 – tail -n [linenum]
[shiming@redhat ~]$ tail -n 5 /etc/passwd
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
oprofile:x:16:16:Special user account to be used by OProfile:/var/lib/oprofile:/sbin/nologin
tcpdump:x:72:72::/:/sbin/nologin
shiming:x:1000:1000:Shiming Liu:/home/shiming:/bin/bash
打印整个文件内容 – cat [filename]
[shiming@redhat ~]$ tail /etc/passwd
文件管理
linux 文件结构
man 自带帮助页:man hier

文件结构标准
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
fhs-2.3.pdf
http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
| 位置 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| /usr | 安装软件、共享的库,包括文件和静态只读程序数据。重要的子目录有: -/usr/bin:用户命令。 -/usr/sbin:系统管理命令。 -/usr/local:本地自定义软件。 |
| /etc | 特定于此系统的配置文件, 静态的永久系统配置数据。 |
| /var | 特定于此系统的可变数据,在系统启动之间保持永久性。动态变化的文件(如数据库、缓存目录、日志文件、打印机后台处理文档内容和网站内容)可以在 /var 下找到。 |
| /run | 包含动态的、非永久的应用程序运行时数据,自上一次系统启动以来启动的进程的运行时数据。这包括进程 ID 文件和锁定文件,等等。此目录中的内容在重启时重新创建。(此目录整合了旧版 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 中的 /var/run 和 /var/lock。) |
| /home | 普通用户主目录。 |
| /root | root 主目录。 |
| /tmp | 临时文件目录。10 天内未访问、未更改或未修改的文件将自动从该目录中删除。还有一个临时目录 /var/tmp,该目录中的文件如果在 30 天内未曾访问、更改或修改过,将自动删除。 |
| /boot | 开机启动过程中所需的文件。 |
| /dev | 包含特殊的设备文件,供系统使用的物理硬件。 |
| /media | 可移除的设备挂载点,如 cd、vcd、U 盘 |
| /usr/bin | 普通用户命令和实用程序 |
| /usr/sbin/ | 供 root 用户使用的二进制文件 |
打印当前工作目录
[shiming@redhat tmp]$ pwd
/tmp
新建目录 – mkdir
常用参数
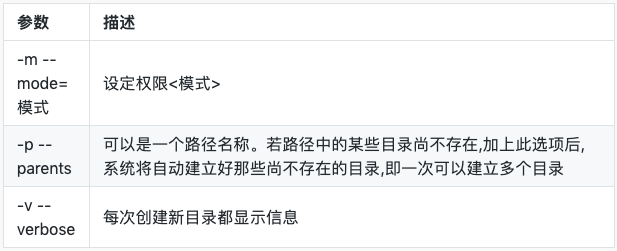
[shiming@redhat ~]$ mkdir tmp
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Public Templates tmp Videos
递归创建目录
mkdir -p /dir/not/exist # 如果/dir或者/dir/not不存在则都会被创建
创建带权限的目录
mkdir -m 744 /dir # /dir的权限会被新建为744
一次性创建多个目录
shiming@pro ➜ /tmp mkdir -p dir1/{dir2/,dir3/{dir3.1,dir3.2}}
shiming@pro ➜ /tmp tree dir1
dir1
├── dir2
└── dir3
├── dir3.1
└── dir3.2
文件列表 – ls
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l #长列表
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -a #显示包括隐藏文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -R #递归列表(包含子文件夹)
[shiming@redhat dir2]$ ls -alR /tmp/dir1 #可组合使用
/tmp/dir1:
total 12
drwxrwxr-x. 3 shiming shiming 4096 Jul 26 22:25 .
drwxrwxrwt. 14 root root 4096 Jul 26 22:26 ..
drwxrwxr-x. 2 shiming shiming 4096 Jul 26 22:26 dir2
/tmp/dir1/dir2:
total 8
drwxrwxr-x. 2 shiming shiming 4096 Jul 26 22:26 .
drwxrwxr-x. 3 shiming shiming 4096 Jul 26 22:25 ..
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 26 22:26 file1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 26 22:26 .file2
ls 可以一次性列出几个文件夹中的文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l Music Pictures Videos #列出N个文件夹
Music:
total 0
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:25 song1.mp3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:25 song2.mp3
Pictures:
total 0
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:26 snap1.jpg
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:26 snap2.jpg
Videos:
total 0
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:27 film1.avi
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 27 23:27 film2.avi
ls -h 列出文件大小为人眼可读的(B,K,M,G)
shiming@pro ➜ asset-platform git:(master) ls -alh
total 24
drwxr-xr-x@ 6 shiming staff 192B Apr 18 10:50 .
drwxr-xr-x@ 22 shiming staff 704B Apr 16 20:13 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 shiming staff 6.0K Apr 22 20:10 .DS_Store
drwxr-xr-x@ 13 shiming staff 416B Apr 22 20:12 .git
-rw-r--r-- 1 shiming staff 36B Apr 16 20:13 README.md
drwxr-xr-x@ 7 shiming staff 224B Apr 22 20:10 docs
切换目录
[shiming@redhat tmp]$ cd /
[shiming@redhat /]$ cd ~/tmp
[shiming@redhat tmp]$ cd - #切到上一个工作目录
/
[shiming@redhat /]$
[shiming@redhat ~]$ cd .. #切到父目录
[shiming@redhat home]$ ls
lost+found shiming
[shiming@redhat ~]$ cd ../.. #从当前位置上移两个级别
[shiming@redhat /]$
新建文件 – touch
[shiming@redhat tmp]$ touch tmp1 #tmp1不存在则新建,存在则将文件的时间戳更新为当前时间
新建多个文件
[shiming@redhat tmp]$ touch file1 file2
使用大括号新建多个文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ touch file{1..5} #如果文件名有规则的话可以这么建
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file4
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file5
删除文件 – rm
常用选项
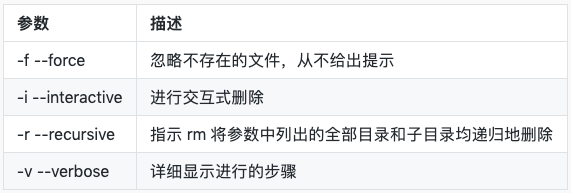
移动文件 – mv
常用选项
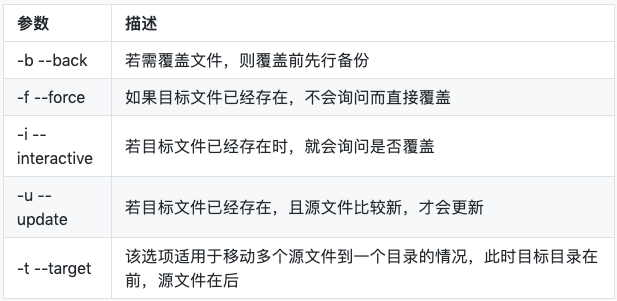
文件管理命令
| 文件管理命令 | 单一来源 | 多来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 复制文件 | cp file1 file2 | cp file1 file2 file3 dir④ |
| 复制文件(目标文件夹不存在) | mkdir -p ~/.litecoin && cp bitcoin.conf litecin.conf | |
| 移动文件 | mv file1 file2① | mv file1 file2 file3 dir④ |
| 删除文件 | rm file1 | rm -f file1 file2 file3⑤ |
| 创建目录 | mkdir dir | mkdir -p part1/part2/dir⑥ |
| 复制目录 | cp -r dir1 dir2② | cp -r dir1 dir2 dir3 dir4④ |
| 移动目录 | mv dir1 dir2③ | mv dir1 dir2 dir3 dir4④ |
| 删除目录 | rm -r dir1② | rm -rf dir1 dir2 dir3⑤ |
*注:
① 结果为重命名。
② 需要使用“递归”选项来处理来源目录。
③ 如果 dir2 存在,则结果为移动。如果 dir2 不存在,则结果为重命名。
④ 最后一个参数必须是目录。
⑤ 请谨慎使用“force”选项,系统将不会提示您确认操作。
⑥使用“创建父级”选项时应小心;无法捕获键入错误。
文件软链接
~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/
修改文件所有者
chown newowner file # 修改file的owner为newowner
chgrp newgroup file # 修改file的group为newowner
chown newowner.newgroup file # 同时修改file的owner
修改文件权限
chmod +x file
chmod -x file
chmod u+x file
chmod
硬盘格式化和挂载
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/25426.html
远程文件传输
在本地 terminal 下执行 scp 命令
- 将本地文件复制到远程
# 将本地文件file1.txt复制到远程服务器家目录下
$ scp -P <sshport> file1.txt root@47.52.241.187:~
- 将本地文件夹复制到远程(-r 选项)
# 将本地文件夹dir1复制到远程家目录
$ scp -P <sshport> -r dir1 root@47.52.241.187:~
- 将远程文件复制到本地
# 将远程文件file2.txt 复制到本地工作目录
$ scp -P <sshport> root@47.52.241.187:~/file2.txt .
- 将远程文件夹复制到本地
# 将远程目录dir1复制到本地当前工作目录
$ scp -P <sshport> -r root@47.52.241.187:~/dir1 .
- 将多个本地文件复制到远程
$ scp -P <sshport> file4 file5 root@47.52.241.187:~
# 只要输一次密码
Enter passphrase for key '/Users/Shiming/.ssh/id_rsa':
file4 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
file5 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
- 将多个远程文件复制到本地
# 几个文件就输几次密码
Shimings-Air:~ Shiming$ scp -P <sshport> root@47.52.241.187:~/{file1.txt,file2.txt} .
Enter passphrase for key '/Users/Shiming/.ssh/id_rsa':
file1.txt 100% 26 0.3KB/s 00:00
Enter passphrase for key '/Users/Shiming/.ssh/id_rsa':
file2.txt 100% 26 0.3KB/s 00:00
rsync vs scp
scp 和 rsync 都是基于 ssh 的文件传输工具,rsync 传输速度更快,但是 rsync 需要在本地和远程都安装,而 scp 一般都原生支持。
远程到本地
rsync -avW -e 'ssh -p 22' user@remote-server:/path/on/remote /path/on/local
scp -P 22 user@remote-server:/path/on/remote /path/on/local
本地到远程
rsync -avW -e 'ssh -p 22' /path/to/local/file user@remote-server:/path/on/remote
scp -P 22 /path/to/local/file user@remote-server:/path/on/remote
用户管理
添加用户
使用useradd命令新增用户,用户初始状态是 lock 的,需要另外使用passwd username来手动设置用户密码,而且用户家目录不会默认创建,除非用-m或-d指定家目录。
# 新增用户
$ useradd shiming
# 修改用户密码
$ passwd shiming
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
# 切换用户家目录(此时家目录不存在)
$ su - shiming
No directory, logging in with HOME=/
# 使用管理员账户为新用户建立家目录
$ su - root
$ sudo mkdir /home/shiming
$ sudo chown shiming:shiming /home/shiming
# 新增用户alice,自动生成家目录,指定默认shell为bash
useradd -m alice -s /bin/bash
总的来说useradd是一个 lowlevel 的新增用户操作,建议使用adduser来新增用户,会有交互式的命令行一次性设置好用户的属性。
$ adduser alice
参考资料:https://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
修改用户
参考资料:https://www.tecmint.com/usermod-command-examples/
修改密码 – passwd
[shiming@red-hat-enterprise-linux ~]$ passwd #修改当前用户密码
更改用户 shiming 的密码 。
为 shiming 更改 STRESS 密码。
(当前)UNIX 密码:
新的 密码:
切换用户
su 切换到 root 用户
su anotheruser 将当前用户的环境变量带到新用户下
su - anotheruser 使用新用户的环境变量
锁住用户
root@tool1:~# passwd -l bot #-l means lock, lock后仍可以使用su - username切换用户
删除用户(连同用户 home 目录)
deluser --remove-home tecmint [On Debian and its derivatives]
userdel --remove tecmint [On RedHat/CentOS based systems]
如果要更严谨的删除用户可以参考 https://www.tecmint.com/delete-remove-a-user-account-with-home-directory-in-linux/
- 锁住账号,这样就无法登陆
- 查看用户进程
- 杀死用户进程
- 备份用户家目录
- 删除用户和家目录
查看当前登录用户
w命令可以查看当前登录用户
shiming@pro ➜ ~ w
23:22 up 12:42, 3 users, load averages: 2.12 1.77 1.84
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE WHAT
shiming console - 10:40 12:41 -
shiming s001 - 11:19 - w
shiming s002 - 10:55 1 ssh root@ubuntu
查看登录记录
last,last <user_name>可以查看登录记录,包括重启/关机记录
shiming@pro ➜ ~ last
shiming ttys001 Tue Mar 26 11:19 still logged in
shiming ttys002 Tue Mar 26 10:55 still logged in
shiming ttys001 Tue Mar 26 10:53 - 10:53 (00:00)
shiming console Tue Mar 26 10:40 still logged in
reboot ~ Tue Mar 26 10:40
shutdown ~ Tue Mar 26 10:17
禁止用户 ssh 登录
编辑/etc/ssh/sshd_config文件,在最后加上DenyUsers配置(如已存在,复用即可)
# deny user ssh login
DenyUsers user1 user2 user3
重启 ssh 服务
sudo systemctl reload ssh
用户不能通过 ssh 登录了,但是可以通过已登录的账号su - user1去切换到 user1
禁止密码登录,仅支持证书
编辑/etc/ssh/sshd_config文件,
- 如果是禁止 root 用户密码登录(但支持证书登录)
# Authentication:
# yes - 允许root登录 no-不允许root登录 prohibit-password-禁止root使用密码登录
PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
- 如果是禁止个别用户、用户组
在最后加上Match段,在里面加上
# disable ssh login by password for some user
Match User user1
PasswordAuthentication no
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
# disable ssh login by password for some group
Match Group group1
PasswordAuthentication no
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
- 如果禁止所有用户密码登录,将以下参数都改为 no
PasswordAuthentication no
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
重启 ssh 服务
sudo systemctl reload ssh
无证书登录时会报错
$ ssh shiming@ubuntu
shiming@ubuntu: Permission denied (publickey).
新建用户默认使用 zsh
如果使用adduser命令新增用户,该命令的配置文件是/etc/adduser.conf,修改该文件将默认
DSHELL=/bin/sh
修改为
DSHELL=/bin/zsh
如果使用useradd添加用户则修改/etc/default/useradd
SHELL=/bin/sh
改为
SHELL=/bin/zsh
通过以上步骤,新用户确实默认使用 zsh,但是因为没有配置~/.zshrc文件,新用户在首次登陆的时候 zsh 会出以下提示,不是太友好:
This is the Z Shell configuration function for new users,
zsh-newuser-install.
You are seeing this message because you have no zsh startup files
(the files .zshenv, .zprofile, .zshrc, .zlogin in the directory
~). This function can help you with a few settings that should
make your use of the shell easier.
You can:
(q) Quit and do nothing. The function will be run again next time.
(0) Exit, creating the file ~/.zshrc containing just a comment.
That will prevent this function being run again.
(1) Continue to the main menu.
(2) Populate your ~/.zshrc with the configuration recommended
by the system administrator and exit (you will need to edit
the file by hand, if so desired).
--- Type one of the keys in parentheses ---
linux 可以支持在新建用户时同时将一些文件放到新用户的家目录下,在配置文件/etc/adduser.conf和/etc/default/useradd中都定义了一个参数
SKEL=/etc/skel
这个路径的含义就是,凡是放到这个目录下的文件,都会拷贝到新用户家目录。
新建用户 blog 做测试,注意Copying files from /etc/skel会有这一句。
root@sz ➜ ~ adduser blog
Adding user `blog' ...
Adding new group `blog' (1001) ...
Adding new user `blog' (1001) with group `blog' ...
Creating home directory `/home/blog' ...
Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...
服务管理
systemd vs init.d
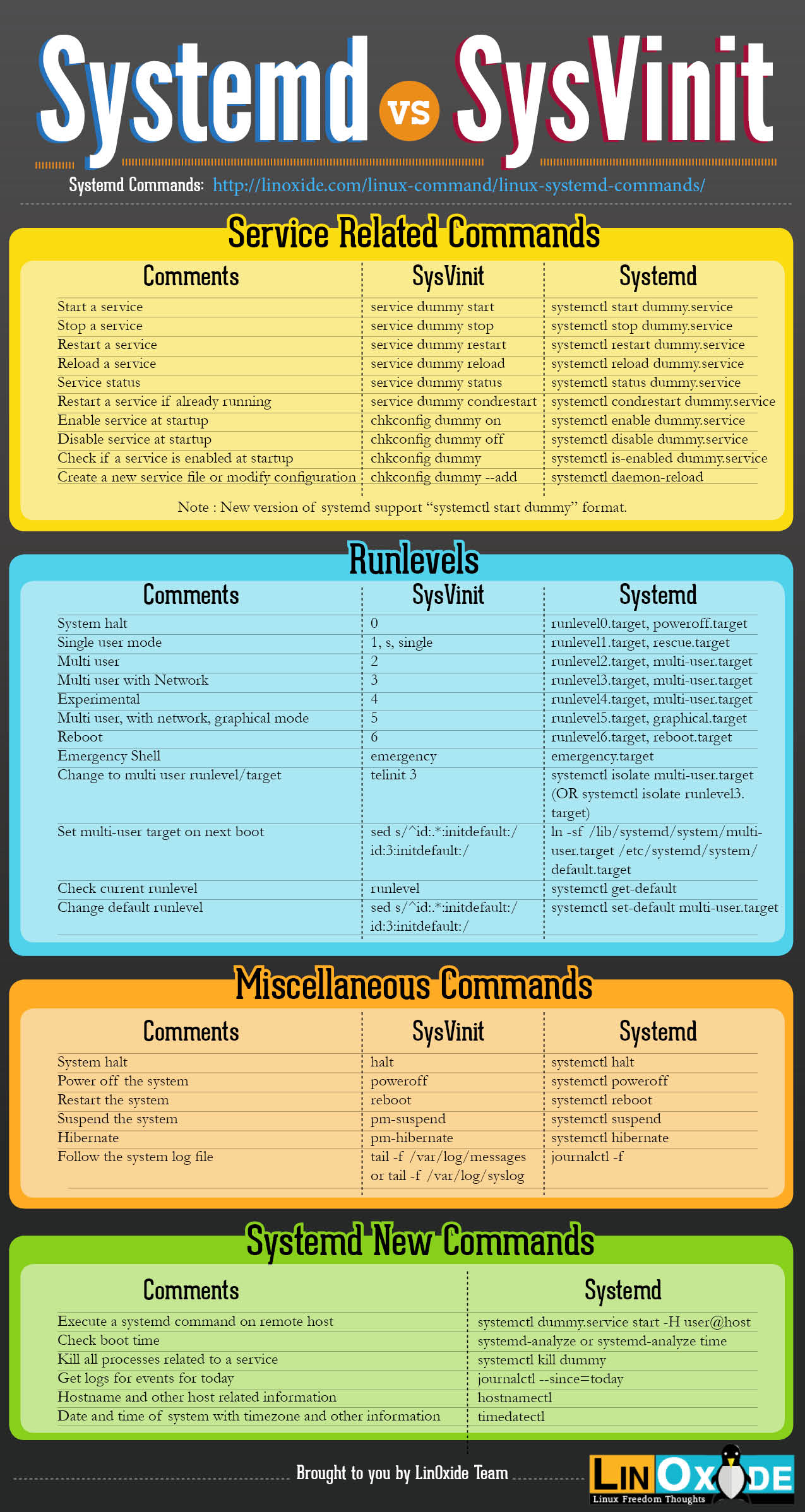
软件安装
二进制包
tar xzf bitcoin-0.14.2-x86_64-linux-gnu.tar.gz
sudo install -m 0755 -o root -g root -t /usr/local/bin bitcoin-0.14.2/bin/*
-m 设置二进制文件权限
-o 设置 owner
-g 设置 group
-t 设置 install 目录
最后一个目录为源目录
命令替换
当命令包含反引号(注意,不是单引号),或\$(command)时,允许命令替换
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo today is `date +%A` #反引号和单引号容易引起混淆
today is Saturday
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo today is $(date +%A) #建议使用$(command)
today is Saturday
命令历史
打印命令行历史
[shiming@redhat ~]$ history
189 wc -l /etc/passwd
190 man wc
191 ls /etc/passwd
192 su
193 history
194 ls /etc/passwd
195 mkdir tmp
196 ls /etc/passwd
197 man wc
198 history
执行历史命令行
193 history
194 ls /etc/passwd
195 mkdir tmp
196 ls /etc/passwd
197 man wc
198 history
[shiming@redhat ~]$ !194 #!+编号 可以执行历史命令行
ls /etc/passwd
/etc/passwd
[shiming@redhat ~]$ !m #!+string 执行最近的一个以m开头的命令行,即 man wc
搜索命令历史
搜索ctrl + r , 取消搜索 ctrl + g
后台运行命令
nohup 后台运行命令
nohup command &
$ nohup geth --testnet --datadir /mnt/ethereum/ --syncmode "full" --rpc --ws &
如果要让正在运行的”前台任务”变为”后台任务”,可以先按 ctrl + z,然后执行 bg 命令(让最近一个暂停的”后台任务”继续执行)
守护进程
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/02/linux-daemon.html
systemd
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html
systemd 示例配置 1
[Unit]
Description=ropsten
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
LimitNOFILE=8192
WorkingDirectory=/mnt/disk2/ethereum/ropsten/
ExecStart=/usr/bin/geth --testnet --syncmode=full --datadir "/mnt/disk2/ethereum/ropsten" --rpc --rpcapi "eth,net,web3,admin,miner,debug,personal,txpool,db,shh" --rpccorsdomain '*' --rpcaddr 127.0.0.1 --rpcport 8540 --port 30300
Restart=always
User=bot
Group=bot
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemd 示例配置 2
[Unit]
Description=openresty A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -q -g 'daemon on; master_process on;'
ExecStart=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;'
ExecReload=/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' -s reload
ExecStop=-/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/start-stop-daemon --quiet --stop --retry QUIT/5 --pidfile /run/nginx.pid
TimeoutStopSec=5
KillMode=mixed
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
新增一个 service 后来设置开机启动
每一个 Unit 都有一个配置文件,告诉 Systemd 怎么启动这个 Unit 。
Systemd 默认从目录/etc/systemd/system/读取配置文件。但是,里面存放的大部分文件都是符号链接,指向目录/usr/lib/systemd/system/,真正的配置文件存放在那个目录。
systemctl enable 命令用于在上面两个目录之间,建立符号链接关系。
$ sudo systemctl enable clamd@scan.service
# 等同于
$ sudo ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/clamd@scan.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/clamd@scan.service'
如果配置文件里面设置了开机启动,systemctl enable 命令相当于激活开机启动。
与之对应的,systemctl disable 命令用于在两个目录之间,撤销符号链接关系,相当于撤销开机启动。
$ sudo systemctl disable clamd@scan.service
列出所有配置文件
# 列出所有配置文件
$ systemctl list-unit-files
# 列出指定类型的配置文件
$ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
这个命令会输出一个列表
$ systemctl list-unit-files
UNIT FILE STATE
chronyd.service enabled
clamd@.service static
clamd@scan.service disabled
这个列表显示每个配置文件的状态,一共有四种。
enabled:已建立启动链接
disabled:没建立启动链接
static:该配置文件没有[Install]部分(无法执行),只能作为其他配置文件的依赖
masked:该配置文件被禁止建立启动链接
# 注意,从配置文件的状态无法看出,该 Unit 是否正在运行。这必须执行前面提到的systemctl status命令。
启动服务
systemctl start xxx.service
查看服务状态
systemctl status xxx.service
reload systemctl 配置
systemctl daemon-reload #一旦修改配置文件,就要让 SystemD 重新加载配置文件,然后重新启动,否则修改不会生效。
重启服务
systemctl restart xxx.service
停止服务
systemctl stop xxx.service
看所有 systemctl 的日志(启动失败的时候可以来这里看)
journalctl -xef
看指定 service 的日志
journalctl -u servicename
网络
端口号说明:
| 端口号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 0~1023 | the Well Known Ports, also referred to as System Ports. |
| 1024~49151 | the Registered Ports, also known as User Ports. |
| 49152~65535 | the Dynamic Ports, also referred to as the Private Ports. |
1024 前的端口绑定需要 root 权限才可以
查看服务和端口绑定信息:
$ cat /etc/services
列出所有打开的端口或正在运行的端口(包括 TCP/UDP):
-l – prints only listening sockets
-n – shows port number
-t – enables listing of tcp ports
-u – enables listing of udp ports
-p – display PID/Program name for sockets
$ netstat -lntup列出所有 tcp/udp、端口、pid、程序名,比较实用
$ netstat -lntu
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:18333 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8545 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8546 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::18333 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::30303 :::* LISTEN
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:*
udp 0 0 172.31.42.181:123 0.0.0.0:*
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:123 0.0.0.0:*
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:123 0.0.0.0:*
udp6 0 0 :::30303 :::*
udp6 0 0 :::123 :::*
以下服务是只对 localhost 相应端口服务的,外网访问不到
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp6 0 0 :::18333 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::30303 :::* LISTEN
或使用 ss -lntu
$ ss -lntu
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:68 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 172.31.42.181:123 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:123 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:123 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 :::30303 :::*
udp UNCONN 0 0 :::123 :::*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:18333 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8545 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8546 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 :::18333 :::*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 :::30303 :::*
重启网络 – ubuntu
sudo service networking restart
网络链路测试
ping 不通或丢包严重时需要进行网络链路测试,定位问题
https://help.aliyun.com/knowledge_detail/40573.html
推荐使用mtr命令
查看端口是否打开
1.你可以使用 lsof 命令来查看某一端口是否开放。查看端口可以这样来使用,我就以 80 端口为例:
lsof -i:80
如果有显示说明已经开放了,如果没有显示说明没有开放
2.netstat -aptn 执行看看,是否监听在 0.0.0.0:3306 3.
netstat -nupl (UDP 类型的端口)
netstat -ntpl (TCP 类型的端口)
例如
4.telnet ip 端口号 方式测试远程主机端口是否打开
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37975886/article/details/78405808?utm_source=copy
阿里云安全组策略
如果阿里云安全组里没有开放端口,即便服务在本机端口绑定了,外网也无法访问
shiming@pro ➜ telnet 120.79.226.111 9009
Trying 120.79.226.111...
telnet: connect to address 120.79.226.111: Operation timed out
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host
防火墙
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw status verbose #查看防火墙详情
Status: inactive #未开启
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow 8545/tcp #允许端口tcp访问
Rules updated
Rules updated (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow 8546/tcp
Rules updated
Rules updated (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow 8545/udp #允许端口udp访问
Rules updated
Rules updated (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow 8546/udp
Rules updated
Rules updated (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw status verbose
Status: inactive
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw enable #开启防火墙
Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? y
Firewall is active and enabled on system startup
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow http #开启80端口(http)访问
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow https #开启443端口(https)访问
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw allow ssh #开启22端口(ssh)访问
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo service networking restart
root@iZj6c48apyeg9dvouqz3uxZ:~# sudo ufw status verbose
Status: active
Logging: on (low)
Default: deny (incoming), allow (outgoing), disabled (routed)
New profiles: skip
To Action From
-- ------ ----
8545/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
8546/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
8545/udp ALLOW IN Anywhere
8546/udp ALLOW IN Anywhere
80 ALLOW IN Anywhere
443 ALLOW IN Anywhere
22 ALLOW IN Anywhere
8545/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
8546/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
8545/udp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
8546/udp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
443 (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
22 (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
网络测试
Shimings-Air:~ Shiming$ traceroute -p 8545 47.75.70.201
traceroute to 47.75.70.201 (47.75.70.201), 64 hops max, 52 byte packets
1 172.16.0.1 (172.16.0.1) 4.037 ms 1.054 ms 1.719 ms
2 192.168.5.1 (192.168.5.1) 5.688 ms 8.667 ms 6.993 ms
3 100.64.0.1 (100.64.0.1) 16.788 ms 5.867 ms 7.902 ms
4 213.106.38.59.broad.fs.gd.dynamic.163data.com.cn (59.38.106.213) 9.796 ms 8.975 ms 8.774 ms
5 183.56.65.62 (183.56.65.62) 13.150 ms 10.301 ms
183.56.65.66 (183.56.65.66) 11.280 ms
6 59.43.80.21 (59.43.80.21) 12.356 ms 10.645 ms 11.649 ms
7 59.43.130.106 (59.43.130.106) 12.012 ms 51.356 ms 43.798 ms
8 59.43.187.126 (59.43.187.126) 16.115 ms
59.43.187.122 (59.43.187.122) 13.389 ms
59.43.187.150 (59.43.187.150) 11.819 ms
9 59.43.187.178 (59.43.187.178) 16.522 ms
59.43.183.106 (59.43.183.106) 21.514 ms
59.43.188.126 (59.43.188.126) 18.220 ms
10 59.43.249.10 (59.43.249.10) 17.732 ms
59.43.186.126 (59.43.186.126) 22.963 ms
59.43.186.122 (59.43.186.122) 14.746 ms
11 210.48.139.70 (210.48.139.70) 21.244 ms
210.48.136.158 (210.48.136.158) 19.783 ms
203.100.48.254 (203.100.48.254) 22.733 ms
12 * * *
13 11.211.16.137 (11.211.16.137) 24.828 ms
11.211.16.105 (11.211.16.105) 22.569 ms
11.211.20.165 (11.211.20.165) 30.418 ms
14 * * *
15 * * *
16 * * *
17 * * *
查看网速
使用nload命令可以查看网络负荷,实时显示网速,按 enter 可以切换网卡
nload比较简洁,只显示总网速,nethogs可以按进程显示网络占用,类似htop
编辑命令行
分隔同一行中的命令
| shell 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ctrl+a | 跳到命令行开头 |
| ctrl+e | 跳到命令行结尾 |
| ctrl+u | 删除光标前内容 |
| ctrl+k | 删除光标后内容 |
| ctrl+左箭头 | 向左跳一字 |
| ctrl+右箭头 | 向右跳一字 |
| ctrl+r | 在命令行历史中搜索某一模式命令 |
| ; | 分隔同一行中的命令 |
| Esc + . | 复制以前命令的最后一个参数 |
bash 配置文件
执行顺序: /etc/profile -> (~/.bash_profile | ~/.bash_login | ~/.profile) -> ~/.bashrc -> /etc/bashrc -> ~/.bash_logout 见参考一
| file | Interactive login | Interactive non-login | Script | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /etc/profile | A | system wide version of ~/.profit, execute once when user login. Executed only for interactive shells | ||
| /etc/profile.d/* | A | user defined /etc/profile, invoked by /etc/profile | ||
| /etc/bashrc or /etc/bash.bashrc | A | system wide version of ~/.bashrc. Executed for both interactive and non-interactive shells. In fact in Ubuntu the /etc/profile calls the /etc/bashrc directly | ||
| ~/.bashrc | B | user defined shell config | ||
| ~/.bash_profile | B1 | |||
| ~/.bash_login | B2 | |||
| ~/.profile | B3 | |||
| BASH_ENV | A | |||
| ~/.bash_logout | C |
查看环境变量
查看所有环境变量使用 printenv 命令
➜ ~ printenv
alias
别名可以定义在.zshrc 或.bashrc 中方便一些操作
# add python3.7 to path
export PATH=/usr/local/Cellar/python/3.7.1/bin:$PATH
export PATH=/usr/local/Cellar/python/3.7/bin:$PATH
alias pip3='python3 -m pip'
alias python2="/usr/bin/python"
# alias cleos in docker
alias cleos='docker exec -it eosio /opt/eosio/bin/cleos --url http://127.0.0.1:7777 --wallet-url http://127.0.0.1:5555'
# alias md_to_json
alias mtj='md_to_json'
# alias for clear
alias cl='clear'
# alias for tldr
alias sman='tldr'
# alias for go to defang dir
alias defang='cd /Users/shiming/Nutstore/21-defang'
# alias for go to jianguoyun dir
alias jianguoyun='cd /Users/shiming/Nutstore'
# alias for go to myrepo dir
alias myrepo='cd /Users/shiming/Nutstore/00-myrepo'
export
bash 内建命令,使得子进程可以复用父进程的环境变量。通过命令行敲的 export 命令,不管是导入还是删除都是临时的。如果需要永久保持有效需要写在~/.bashrc 等配置文件中。
unset 环境变量
unset命令可以删除 export 的环境变量
➜ ~ export TMPVAR="XX"
➜ ~ printenv TMPVAR
XX
➜ ~ unset TMPVAR
➜ ~ printenv TMPVAR
查看单个环境变量
➜ ~ printenv HOME
/Users/shiming
常见环境变量
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| EDITOR | The program to run to perform edits. |
| HOME | The Home directory of the user. |
| LOGNAME | The login name of the user. |
| The location of the user’s local inbox. | |
| OLDPWD | The previous working directory. |
| PATH | A colon separated list of directories to search for commands. |
| PAGER | This program may be called to view a file. |
| PS1 | PS1 The primary prompt string. |
| PWD | The present working directory. |
| USER | The username of the user. |
PATH
PATH环境变量决定了系统寻找执行程序时的路径,默认的环境变量如下
john@ubuntu:~$ echo $PATH
/home/john/bin:/home/john/.local/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games
/usr/bin 和/usr/local/bin 的区别:
首先注意 usr 指 Unix System Resource,而不是 User
然后通常:
/usr/bin 下面的都是系统预装的可执行程序,会随着系统升级而改变。
/usr/local/bin 目录是给用户放置自己的可执行程序的地方,推荐放在这里,不会被系统升级而覆盖同名文件。
~/.local目录是使用 systemd linux 发行版都会有的一个目录
参数说明
-p
List of all names that are exported in the current shell
-n
Remove names from export list
-f
Names are exported as functions
export 作用解析
没用 export 前
[shiming@redhat ~]$ name=shiming #设置变量name=shimiing
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo $name #在当前进程下输出
shiming #正确输出
[shiming@redhat ~]$ bash #新开一个进程
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo $name #在新开的进程输出$name
#无效
[shiming@redhat ~]$
用了 export 后
[shiming@redhat ~]$ name=shiming #设置变量name=shiming
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo $name #当前进程输出
shiming #正确输出
[shiming@redhat ~]$ export name #export变量
[shiming@redhat ~]$ bash #新开进程
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo $name #再次输出
shiming #正确输出
append to the PATH
给 PATH 加一个路径,用冒号分隔
$ export PATH=$PATH:/home/himanshu/practice/
固化环境变量
export name="xiongxiong" #在~/.bashrc文件末尾加上这句
[shiming@redhat shiming]$ echo $name #打印为空
[shiming@redhat shiming]$ source .bashrc #执行.bashrc
[shiming@redhat shiming]$ echo $name #打印有值
xiongxiong
[shiming@redhat shiming]$ unset name #如果不想用这个环境变量了,用unset暂时删除
[shiming@redhat shiming]$ echo $name #打印为空
局部和全局环境变量设置
参考这里
进程管理
查看进程资源占用
使用命令top(或 htop,需要安装)
Processes: 501 total, 2 running, 499 sleeping, 2532 threads 09:39:06
Load Avg: 2.68, 1.92, 1.79 CPU usage: 1.26% user, 1.42% sys, 97.30% idle
SharedLibs: 229M resident, 47M data, 86M linkedit.
MemRegions: 171203 total, 8320M resident, 84M private, 1873M shared.
PhysMem: 16G used (6889M wired), 118M unused.
VM: 2489G vsize, 1121M framework vsize, 30538579(0) swapins, 32834518(0) swapouts.
Networks: packets: 60080455/70G in, 68155895/7815M out. Disks: 6097134/243G read, 6811848/392G written.
PID COMMAND %CPU TIME #TH #WQ #PORTS MEM PURG CMPRS PGRP PPID STATE BOOSTS
44018 top 5.0 00:02.23 1/1 0 26 6032K 0B 0B 44018 33399 running *0[1]
44017 sleep 0.0 00:00.00 1 0 10 328K 0B 0B 26499 26726 sleeping *0[1]
44000 quicklookd 0.0 00:00.16 4 1 88 5104K 28K 0B 44000 1 sleeping 0[0]
43947 com.apple.iC 0.0 00:00.14 2 1 59 3032K 0B 256K 43947 1 sleeping 0[0]
43904 ocspd 0.0 00:00.02 2 1 36 1912K 0B 0B 43904 1 sleeping *0[1]
43881 Google Chrom 0.0 00:00.79 10 2 73 29M 4096B 9560K 1123 1123 sleeping *0[3]
43880 Google Chrom 0.0 00:05.02 16 1 125 98M 0B 19M 1123 1123 sleeping *0[3]
43879 Google Chrom 0.0 00:00.31 16 1 122 17M 0B 12M 1123 1123 sleeping *0[3]
43769 MTLCompilerS 0.0 00:00.06 3 3 27 16K 0B 10M 43769 1 sleeping 0[2]
43764 com.apple.pr 0.0 00:02.17 4 1 274 5948K 0B 21M 43764 1 sleeping *0[598]
43763 MTLCompilerS 0.0 00:00.07 3 3 27 12K 0B 10M 43763 1 sleeping 0[2]
43757 System Prefe 0.0 00:02.70 4 1 296 5632K 8192B 18M 43757 1 sleeping *0[304]
43729 com.apple.no 0.0 00:00.04 2 1 44 28K 0B 1424K 43729 1 sleeping 0[1]
43727 mdworker 0.0 00:00.07 3 1 54 52K 0B 3232K 43727 1 sleeping *0[1]
43711 Google Chrom 0.0 00:25.45 17 1 133 44M 0B 125M 1123 1123 sleeping *0[24]
43004 Google Chrom 0.2 04:07.35 19 1 150 208M 0B 62M 1123 1123 sleeping *0[26]
进程后台运行
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| command & | 进程后台运行 |
| ctrl + c | 停止前台运行进程 |
| ctrl + z | 挂起当前进程 |
| bg | 讲挂起的进程放在后台继续运行(需配合 ctrl + z 使用) |
| bg [%num] | 将进程放在后台运行 |
| fg [%num] | 将进程放在前台运行 |
| kill -l | 查看所有中断信号 |
| kill -9 pid | 杀死进程 |
| jobs | 查看 jobs |
查看指定进程
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ ps -p 1 #查看pid = 1的进程信息
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:03 systemd
打印当前进程 id
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ echo $$ #两个美元符号打印当前进程名
19376
查询子进程信息
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ echo $$ #当前进程
19376
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ bash #新起一个子进程
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ echo $$ #获取子进程id
21139
[shiming@redhat profile.d]$ ps --ppid 19376 #查看子进程信息
PID TTY TIME CMD
21139 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
进程前台/后台运行切换
Bg, Fg, &, Ctrl-Z – 5 Examples to Manage Unix Background Jobs
vim
系统自带教程
[shiming@redhat ~]$ vimtutor
vim 复制内容到 Mac 系统剪贴板
mac 自带的 vim 位于/usr/bin 目录下,这个版本不支持将 vim 中的内容复制到系统剪贴板
如何查看是否支持复制到剪贴板:
vim --version
如果出现+clipboard则支持,出现-clipboard则不支持
所以需要自己重新安装 vim, brew install vim --with-client-server
安装后需要做两件事:
- 做一个软连接到/usr/local/bin, 这样就会使用新装的 vim,因为/usr/local/bin 在 path 中比/usr/bin 更靠前
ln -sf /usr/local/Cellar/vim/8.1.0600_1/bin/vim /usr/local/bin/vim
ln -sf /usr/local/Cellar/vim/8.1.0600_1/bin/vim /usr/local/bin/vi
2.还需要修改~/.vimrc 文件,加上下面这行
set clipboard=unnamed
以后就可以在 vim 中 visual 模式选中文字进行复制(yank)了
写 read-only 文件
有时没有用 sudo 打开文件,编辑后保存不了,会提示 read-only,可以用以下命令将文件写进去,不用退出文件再 sudo 打开。
:w !sudo tee %
命令解释:
:w – write
!sudo – call shell sudo command
tee – the output of write (:w) command is redirected using tee
% – current file name
相对行号
set relativenumber可以开启相对行号
以下.vimrc 配置可以在 normal 模式下显示相对行号,insert 模式下现在正常行号
set nu
augroup relative_numbser
autocmd!
autocmd InsertEnter * :set norelativenumber
autocmd InsertLeave * :set relativenumber
augroup END
vscode vim 插件设置
https://medium.com/@realjohnnylau/vscode-vim-easymotion-%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE-6b64bba642cf
vim normal 模式和插入模式指针形状
normal 模式和插入模式指针形状如果没有区别(normal 模式方块,插入模式一根竖线)可以在.vimrc 文件中进行设置
参考 https://vim.fandom.com/wiki/Change_cursor_shape_in_different_modes
常用命令列表
| 操作 | 命令 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 光标左移 | h | |
| 光标右移 | l | |
| 光标下移 | j | |
| 光标上移 | k | |
| 光标移到当前屏幕顶部 | H | H for Home |
| 光标移到当前屏幕中部 | M | M for Middle |
| 光标移到当前屏幕底部 | L | L for Last |
| 光标跳到下一个句子 | ) | |
| 光标跳到上一个句子 | ( | |
| 光标跳到下一个段落 | } | |
| 光标跳到上一个段落 | { | |
| 当前光标插入 | i | |
| 当前光标后插入 | a | |
| 复制行 | yy or Y | |
| 剪切行 | dd | |
| 剪切两行 | 2dd | |
| 粘贴(到光标后) | p | p for paste |
| 粘贴(到光标前) | P(大写) | |
| 显示行号 | :set number | 简写:set nu |
| 不显示行号 | :set nonumber | 简写:set nu! |
| 显示相对行号 | :set relativenumber | 简写:set rnu |
| 不显示相对行号 | :set norelativenumber | 简写:set rnu! |
| 显示所有设置项 | :set all | |
| 显示用户设置 | :set | |
| 删除到本单词结尾(包括紧跟着的空格) | dw | |
| 删除到两个单词结尾(包括紧跟着的空格) | d2w | 以此类推 |
| 删除到本单词结尾(不包括紧跟的空格) | de | |
| 删除到两个单词结尾(不包括紧跟的空格) | d2e | 以此类推 |
| 删除到本行末尾 | d$ | |
| 删除到本行开头 | d^ | |
| 删除到文件末尾 | dG | |
| 删除两个引号/括号中的内容(不包括引号) | di” 或 di) | i for inside |
| 删除两个引号/括号中的内容(包括引号) | da” 或 da) | |
| 删除到文件开头(包括光标所在行) | dgg/d1G | |
| 删除到指定字符(包含字符) | dfX | 删除到 X,包含 X |
| 删除到指定字符(不包含字符) | dtX | 删除到 X,不包含 X |
| 删除到指定正则匹配到的字符(不包含字符) | d/regex | |
| 反向删除到指定字符(包含字符) | dFX | 删除到 X,包含 X |
| 反向删除到指定字符(不包含字符) | dTX | 删除到 X,不包含 X |
| 删除一行并进入插入模式 | cc | |
| 删除到单词结尾并进入插入模式 | ce | 方便修改该单词,c for change |
| 删除到本行末尾并进入插入模式 | c$ 或 C(大写) | |
| 整行向右缩进 | >> | |
| 整行向左缩进 | << | |
| 撤销 | u | |
| 撤销之撤销 | ctrl + r | r for redo |
| 保存 | :w | |
| 另存为 | :w + filename | 将目前编辑的文件另存为 filename |
| 保存并退出 | :wq or :ZZ | |
| 不保存退出 | :q! | q for quit |
| 保存只读文件 | :w !sudo tee % | |
| 跳到下一词首 | w | w for word |
| 跳到上一词首 | b | b for back |
| 跳到下 2 个词首 | 2w | 以此类推 |
| 跳到词尾 | e | e for end |
| 跳到下一词尾 | 2e | 以此类推 |
| 替换光标处字符 | r + 新字符 | |
| 行内字符查找 | f + 字符 + ;(optional, 可将光标跳到下一个匹配项) | |
| 行内字符查找 (反向) | F + 字符 + ;(optional, 可将光标跳到下一个匹配项) | |
| 跳到文本末尾 | G | |
| 跳到文本开头 | gg | |
| 跳到指定行 | 行号 + G | |
| 向下搜索 | / + keyword | |
| 向上搜索 | ? + keyword | |
| 查找下一个 | n | |
| 查找上一个 | N | |
| 搜索高亮 | :set hls | |
| 跳到光标上一个所在的位置 | ctrl + o | o for older |
| 跳到光标下一个所在的位置 | ctrl + i | |
| 找到对称的另一半括号(大中小括号都行) | 将光标置于括号上然后按% | |
| 替换光标行第一个匹配项 | :s/old/new/ | old 为待替换字符,new 为新字符 |
| 替换光标行所有匹配项 | :s/old/new/g | g for global |
| 替换指定行所有匹配项 | :#,#s/old/new/g | 两个井号代表开始行和结束行 |
| 全局替换(无确认) | :%s/old/new/g | |
| 全局替换(逐个确认) | :%s/old/new/gc | c for comfirm |
| 执行外部命令 | :! + command | 举例 :!ls :!rm file |
| 进入 visual 模式 | v | 进入 visual 模式后可以通过移动光标选中文字 |
| 复制选中文字 | visual 模式选中 + y | |
| 删除选中文字 | visual 模式选中 + d | |
| 选中文字另存为新文件 | visual 模式选中 + :w + 新文件名 | |
| 在光标后插入另一文件的内容 | :r + filename | 将 filename 附加到光标后 |
| 在光标后插入命令行的标准输出 | :r + !ls -l | 将 ls -l 输出附加到光标后 |
| 在光标下插一空行 | o | o for open, open a line |
| 在光标上插一空行 | O | |
| 标记书签 | ma | 给该行打上标记 a (可以标记 a-z) |
| 跳转到书签行 | ‘a | |
| 跳转到书签行列 | `a | 不仅跳转到行而且跳转到光标所在的列 |
| 标签列表 | :marks | |
| 删除标签 | :delmarks a 或 :delm a | 删除标签 a |
| vim | :set xxx | ‘ic’ ‘ignorecase’ ignore upper/lower case when searching ‘is’ ‘incsearch’ show partial matches for a search phrase ‘hls’ ‘hlsearch’ highlight all matching phrases 给以上选项前加上’no’即可撤销命令 |
| 查看帮助 | :help | 查看帮助时切换窗口 ctrl + w |
| 个性化 vim 配置文件 | :e ~/.vimrc | 查看帮助时切换窗口 ctrl + w |
vim 中文乱码
如果 vim 中文乱码,在用户家目录下新建.vimrc 文件,填入以下内容
set fileencodings=utf-8,gbk,utf-16le,cp1252,iso-8859-15,ucs-bom
set termencoding=utf-8
set encoding=utf-8
也可以在/etc/vim/vimrc 里加在最后,但是这个文件影响所有用户,在自己家目录下的.vimrc 只影响自己
获取帮助
搜索帮助主题
[shiming@redhat ~]$ man -k passwd #搜索与关键字passwd有关的帮助
chpasswd (8) - update passwords in batch mode
fgetpwent_r (3) - get passwd file entry reentrantly
getpwent_r (3) - get passwd file entry reentrantly
gpasswd (1) - administer /etc/group and /etc/gshadow
grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2 (1) - Generate a PBKDF2 password hash.
kpasswd (1) - change a user's Kerberos password
lpasswd (1) - Change group or user password
lppasswd (1) - add, change, or delete digest passwords.
帮助分类
| num | topic | note |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Executable programs or shell commands | 用户命令 |
| 2 | System calls (functions provided by the kernel) | 系统调用 |
| 3 | Library calls (functions within program libraries) | 库函数 |
| 4 | Special files (usually found in /dev) | 特殊文件 |
| 5 | File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd | 文件格式 |
| 6 | Games | 游戏 |
| 7 | Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7) | 惯例、标准和其他 |
| 8 | System administration commands (usually only for root) | 系统管理命令 |
| 9 | Kernel routines [Non standard] | Linux 内核 API |
pinfo
pinfo 提供更详细的帮助文档
[shiming@redhat doc]$ pinfo vim
查看软件包文档
软件包文档储存在/usr/share/doc 目录下,里面包含大量软件包提供的文档说明
创建、查看和编辑文本文件
标准输入、标准输出、标准错误
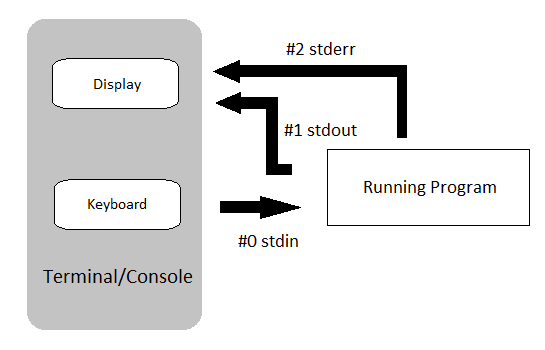
exit code
bash 脚本运行终止时可以返回一个exit code,就像在 C 程序中一样。它也可以返回一个值,这个值可以给脚本的父进程。
每个命令都会返回一个exit status(有时被称为返回状态或退出代码)。成功的命令会返回一个 0,而不成功的命令会返回一个非零值,通常可以解释为错误代码。行为良好的 UNIX 命令、程序和实用程序在成功完成后都会返回 0 的退出代码,但也有一些例外。
同样,脚本中的函数和脚本本身也会返回一个退出状态。函数或脚本中最后执行的命令决定了退出状态。在脚本中,可以使用 exit nnn 命令向 shell 传送 nnn 退出状态(nnn 必须是 0 – 255 范围内的整数)。
查看上一个命令的exit code的方法为echo $?如果运行正常,输出为 0,否则代表出错。
参考资料 Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide
重定向
stdout 重定向,>覆盖写,>>追加写
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echo "hello" > /tmp/hello.txt #输出重定向,新建
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello.txt
hello
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echo "world" >> /tmp/hello.txt #输出重定向,追加
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello.txt
hello
world
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echo "hello world" > /tmp/hello.txt #输出重定向,覆盖
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello.txt
hello world
stderr 重定向
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echox "hello world" 2>/tmp/hello_err.txt #错误重定向,新建
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello_err.txt
bash: echox: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echoy "hello world" 2>>/tmp/hello_err.txt #错误重定向,追加
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello_err.txt
bash: echox: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
bash: echoy: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echoz "hello world" 2 > /tmp/hello_err.txt #重定向符号左右不能空格
bash: echoz: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echoz "hello world" 2>/tmp/hello_err.txt #错误重定向,覆盖
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/hello_err.txt
bash: echoz: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echoz "hello world" 2>/dev/null #将错误信息重定向到/dev/null,从而将它丢弃
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /dev/null #无输出
stdout 和 stderr 一起重定向
$ command >file 2>&1 #重定向stdout和stderr以覆盖同一个文件
$ command &>file #与上面等效(推荐)
$ command >>file 2>&1 #重定向stdout和stderr以附加到同一个文件
$ command &>>file #与上面等效(推荐)
#示例:
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echo "nice day" &>/tmp/nice.txt
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/nice.txt
nice day
[shiming@redhat doc]$ echoa "nice day" &>>/tmp/nice.txt
[shiming@redhat doc]$ cat /tmp/nice.txt
nice day
bash: echoa: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
重定向示例
保存时间戳供以后参考
[shiming@redhat ~]$ date > /tmp/saved_timestamp
将一个日志的后 100 行负责到另一文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ tail -n 100 /var/log/dmesg >/tmp/last_100_boot_msg
将四个文件连接为一个
[shiming@redhat ~]$ cat file1 file2 file3 file4 >/tmp/four_in_one
将文件名列出到文件中
[shiming@redhat ~]$ cat /tmp/filename
将输出附加到现有文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ echo "new line info" >>/tmp/many_lines_of_info
[shiming@redhat ~]$ diff previous_file current_file >>/tmp/tracking_change_made
将错误重定向到文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ find /etc -name passwd 2>/tmp/error
将输出和错误分别定向到不同文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ find /etc -name passwd >/tmp/output 2>/tmp/error
忽略并丢弃错误信息
[shiming@redhat ~]$ find /etc -name passwd >/tmp/output 2>/dev/null
将输出和错误信息一并保存
[shiming@redhat ~]$ find /etc -name passwd &>/tmp/save_both
将输出和错误信息附加保存
[shiming@redhat ~]$ find /etc -name passwd &>>/tmp/save_both
管道

管道示例
单一管道
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls | wc -l #计算文件数
14
管道和重定向组合使用
#将ls -l命令输出前5行重定向到 /tmp.first_five_lines文件
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l | head -n 5 > /tmp/first_five_lines
[shiming@redhat ~]$ cat /tmp/first_five_lines
total 36
drwxr-xr-x. 2 shiming shiming 4096 Mar 3 11:35 Desktop
drwxr-xr-x. 2 shiming shiming 4096 Jan 13 2018 Documents
drwxr-xr-x. 2 shiming shiming 4096 Jan 13 2018 Downloads
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file1
tee
Copy standard input to each FILE, and also to standard output.
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l file* | tee /tmp/saved_output #文件中有保持,stdout也打印
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file4
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file5
[shiming@redhat ~]$ ls -l file* | head -n 2 | tee /tmp/first_two_lines
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 shiming shiming 0 Jul 28 09:41 file2
用户和组
查看当前用户信息
[shiming@redhat ~]$ id
uid=1000(shiming) gid=1000(shiming) groups=1000(shiming),10(wheel) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
passwd 文件格式

- Username: It is used when user logs in. It should be between 1 and 32 characters in length.
- Password: An x character indicates that encrypted password is stored in /etc/shadow file. Please note that you need to use the passwd command to computes the hash of a password typed at the CLI or to store/update the hash of the password in /etc/shadow file.
- User ID (UID): Each user must be assigned a user ID (UID). UID 0 (zero) is reserved for root and UIDs 1-99 are reserved for other predefined accounts. Further UID 100-999 are reserved by system for administrative and system accounts/groups.
- Group ID (GID): The primary group ID (stored in /etc/group file)
- User ID Info: The comment field. It allow you to add extra information about the users such as user’s full name, phone number etc. This field use by finger command.
- Home directory: The absolute path to the directory the user will be in when they log in. If this directory does not exists then users directory becomes /
- Command/shell: The absolute path of a command or shell (/bin/bash). Typically, this is a shell. Please note that it does not have to be a shell.
在 passwd 文件中搜索用户
搜索用户 tom
$ grep tom /etc/passwd
组
与用户一样,组也有名称和编号(GID)。本地组在/etc/group 中定义
主要组
- 每个用户只有一个主要组
- 对于本地用户,主要组通过/etc/passwd 第四个字段定义
- 通常,用户创建的新文件归主要组所有
- 通常,新建用户的主要组是名称与用户相同的新建组,用户是此用户专用组(UPG)的唯一成员
补充组
用户可以是零个或多个补充组的成员。
属于本地组补充成员的用户列在/etc/group 中组条目的最后一个字段中。对于本地组,成员身份由/etc/group 中组条目的最后一个字段中的逗号分隔用户列表确定。
包管理
不同的发行版有不同的包管理程序
| Operating System | Format | Tool(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Debian | .deb | apt, apt-cache, apt-get, dpkg |
| Ubuntu | .deb | apt, apt-cache, apt-get, dpkg |
| CentOS | .rpm | yum |
| Fedora | .rpm | dnf |
| FreeBSD | Ports, .txz | make, pkg |
更新包列表
| System | Command |
|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | sudo apt-get update |
| sudo apt update | |
| CentOS | yum check-update |
| Fedora | dnf check-update |
| FreeBSD Packages | sudo pkg update |
| FreeBSD Ports | sudo portsnap fetch update |
更新已安装的包
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | sudo apt-get upgrade | Only upgrades installed packages, where possible. |
| sudo apt-get dist-upgrade | May add or remove packages to satisfy new dependencies. | |
| sudo apt upgrade | Like apt-get upgrade. | |
| sudo apt full-upgrade | Like apt-get dist-upgrade. | |
| CentOS | sudo yum update | |
| Fedora | sudo dnf upgrade | |
| FreeBSD Packages | sudo pkg upgrade | |
| FreeBSD Ports | less /usr/ports/UPDATING | Uses less to view update notes for ports (use arrow keys to scroll, press q to quit). |
| cd /usr/ports/ports-mgmt/portmaster && sudo make install && sudo portmaster -a | Installs portmaster and uses it to update installed ports. |
搜索包
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | apt-cache search search_string | |
| apt search search_string | ||
| CentOS | yum search search_string | |
| yum search all search_string | Searches all fields, including description. | |
| Fedora | dnf search search_string | |
| dnf search all search_string | Searches all fields, including description. | |
| FreeBSD Packages | pkg search search_string | Searches by name. |
| pkg search -f search_string | Searches by name, returning full descriptions. | |
| pkg search -D search_string | Searches description. | |
| FreeBSD Ports | cd /usr/ports && make search name=package | Searches by name. |
| cd /usr/ports && make search key=search_string | Searches comments, descriptions, and dependencies. |
查看包信息
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | apt-cache show package | Shows locally-cached info about a package. |
| apt show package | ||
| dpkg -s package | Shows the current installed status of a package. | |
| CentOS | yum info package | |
| yum deplist package | Lists dependencies for a package. | |
| Fedora | dnf info package | |
| dnf repoquery –requires package | Lists dependencies for a package. | |
| FreeBSD Packages | pkg info package | Shows info for an installed package. |
| FreeBSD Ports | cd /usr/ports/category/port && cat pkg-descr |
从库中安装包
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | sudo apt-get install package | |
| sudo apt-get install package1 package2 … | Installs all listed packages. | |
| sudo apt-get install -y package | Assumes “yes” where apt would usually prompt to continue. | |
| sudo apt install package | Displays a colored progress bar. | |
| CentOS | sudo yum install package | |
| sudo yum install package1 package2 … | Installs all listed packages. | |
| sudo yum install -y package | Assumes “yes” where yum would usually prompt to continue. | |
| Fedora | sudo dnf install package | |
| sudo dnf install package1 package2 … | Installs all listed packages. | |
| sudo dnf install -y package | Assumes “yes” where dnf would usually prompt to continue. | |
| FreeBSD Packages | sudo pkg install package | |
| sudo pkg install package1 package2 … | Installs all listed packages. | |
| FreeBSD Ports | cd /usr/ports/category/port && sudo make install | Builds and installs a port from source. |
安装包时自动确认加-y选项
sudo apt install -y nginx
从本地安装包
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | sudo dpkg -i package.deb | |
| sudo apt-get install -y gdebi && sudo gdebi package.deb | Installs and uses gdebi to install package.deb and retrieve any missing dependencies. | |
| CentOS | sudo yum install package.rpm | |
| Fedora | sudo dnf install package.rpm | |
| FreeBSD Packages | sudo pkg add package.txz | |
| sudo pkg add -f package.txz | Installs package even if already installed. |
删除一个或多个包
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | sudo apt-get remove package | |
| sudo apt remove package | ||
| sudo apt-get autoremove | Removes unneeded packages. | |
| CentOS | sudo yum remove package | |
| Fedora | sudo dnf erase package | |
| FreeBSD Packages | sudo pkg delete package | |
| sudo pkg autoremove | Removes unneeded packages. | |
| FreeBSD Ports | sudo pkg delete package | |
| cd /usr/ports/path_to_port && make deinstall | De-installs an installed port. |
查看帮助
| System | Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | man apt-get | Updating the local package database and working with packages. |
| man apt-cache | Querying the local package database. | |
| man dpkg | Working with individual package files and querying installed packages. | |
| man apt | Working with a more concise, user-friendly interface to most basic operations. | |
| CentOS | man yum | |
| Fedora | man dnf | |
| FreeBSD Packages | man pkg | Working with pre-compiled binary packages. |
| FreeBSD Ports | man ports | Working with the Ports Collection. |
apt vs apt-get
建议使用 apt 替代 apt-get,apt 是 apt-get 与 apt-cache 的常用命令集成
| apt | apt-get | function |
|---|---|---|
| apt install | apt-get install | Installs a package |
| apt remove | apt-get remove | Removes a package |
| apt purge | apt-get purge | Removes package with configuration |
| apt update | apt-get update | Refreshes repository index |
| apt upgrade | apt-get upgrade | Upgrades all upgradable packages |
| apt autoremove | apt-get autoremove | Removes unwanted packages |
| apt full-upgrade | apt-get dist-upgrade | Upgrades packages with auto-handling of dependencies |
| apt search | apt-cache search | Searches for the program |
| apt show | apt-cache show | Shows package details |
更多资源
This guide covers Ubuntu and Debian package management in detail.
There’s an official CentOS guide to managing software with yum.
There’s a Fedora wiki page about dnf, and an official manual for dnf itself.
This guide covers FreeBSD package management using pkg.
The FreeBSD Handbook contains a section on using the Ports Collection.
常用 bash 命令
find
递归搜索当前目录,名字为 tecmint.txt
# find . -name tecmint.txt
./tecmint.txt
递归搜/home 目录
# find /home -name tecmint.txt
/home/tecmint.txt
不区分小写搜索
# find /home -iname tecmint.txt
./tecmint.txt
./Tecmint.txt
搜索目录名
# find / -type d -name Tecmint
/Tecmint
find -type参数
-type t
True if the file is of the specified type. Possible file types are as follows:
b block special
c character special
d directory
f regular file
l symbolic link
p FIFO
s socket
查找 java 文件
# find . -name '*.java'
person.java
main.java
配合 xargs 使用:递归搜索当前目录,名字为.java 结尾的文件,并附加到 src.txt 中
# find . -name '*.java' | xargs cat >> src.txt
找出 777 权限的文件
# find . -perm 777
找出所有的空文件
find /tmp -type f -empty
找出所有的空文件夹
# find /tmp -type d -empty
找出所有的隐藏文件
# find /tmp -type f -name ".*"
找出某个用户的文件
# find / -user root -name tecmint.txt
找出某个组的文件
# find /home -group developer
找出近 50 天修改的文件
# find / -mtime 50
找出近 50 天打开过的文件
# find / -atime 50
找出 50~100 天内修改的文件
# find / -mtime +50 –mtime -100
1 小时内有文件属性变化
# find / -cmin -60
1 小时文件内容变化
# find / -mmin -60
大于 50 小于 100M 的文件
# find / -size +50M -size -100M
找出并删除大于 10M 的 mp3 文件
# find / -type f -name *.mp3 -size +10M -exec rm {} +
find 找出路径后配合其他命令使用:
# 推荐,并行处理,无需借助管道
find . -exec cmd {} +
# 推荐,并行处理,速度快
find . -print0 | xargs -0 cmd
# 文件名有空格时将不能处理
find . | xargs cmd
# 不推荐,命令一行行执行,不是并行,速度最慢
find . -exec cmd {} \;
参考:
35 个 find 示例
linux find 中的-print0 和 xargs 中-0 的奥妙
sed
sed 的意思是 Stream EDitor,即流式编辑器,sed 命令实现对文件的”增删改查“,玩转 sed 是写自动化脚本必须的基础之一。
sed 遵循简单的工作流:
- 读取(从输入中读取某一行)
- 执行(在某一行上执行 sed 命令)
- 显示(把结果显示在输出中)
- 默认是显示修改后内容,不会修改原文件,除非使用-i 参数。
查找并替换文件中搜索到的内容
linux 下:
sed -i 's/original/new/g' file.txt
mac 下的 sed 命令略有区别,前面还需要指定一个备份文件后缀。
# 以下命令执行完,存在两个文件 file.txt file.txt.bup
sed -i '.bup' 's/original/new/g' file.txt
# 如果不需要备份也可以这么写的
sed -i '' 's/original/new/g' file.txt
awk
http 文件服务器
单可靠的 http 文件服务器 apache2 或者叫 httpd (两者一样),在 ubuntu 中apt install apache2,centos yum install httpd
apache2 的配置文件目录是 /etc/apache2 主配置是 /etc/apache2/apache2.conf 但是其他目录
httpd 的配置文件是 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
安装好后可通过 systemctl start apache2 启动服务
可通过 netstat 查看服务和端口绑定情况
$ netstat -lntpu
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 18256/apache2
对外可访问的文件默认放置在 /var/www/html 目录下,服务的端口默认为 80
但文件可以软链接至 /var/www/html 目录下而不必真的移动过去
文件下载
小文件用 wget <URL>
大文件用 axel -n 20 <URL> 多线程下载,可以把网络跑满
下载后重命名文件 wget -O <newFileName> <fileUrl>
文件压缩和解压
压缩大文件 tar -c --use-compress-program=pigz -f tar.file dir_to_zip
大文件边下载边解压 wget -q -O - <URL> | tar -zxvf -
指定使用pigz解压 tar -I pigz -xvf <FILE>.tar.gz
实用技巧
删除阿里云盾
执行以下命令
wget http://update.aegis.aliyun.com/download/uninstall.sh && chmod +x uninstall.sh && ./uninstall.sh
执行以下命令
wget http://update.aegis.aliyun.com/download/quartz_uninstall.sh && chmod +x quartz_uninstall.sh && ./quartz_uninstall.sh
删除残留
pkill aliyun-service && rm -fr /etc/init.d/agentwatch /usr/sbin/aliyun-service && rm -rf /usr/local/aegis*
屏蔽云盾
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.201.0/28 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.201.16/29 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.201.32/28 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.192/29 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.200/30 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.184/29 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.183/32 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.206/32 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.205/32 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.195/32 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 140.205.225.204/32 -j DROP
ubuntu 安装 mysql
(1)安装
MySQL 是一个小型关系型数据库管理系统,其安装分为服务端与客户端
安装命令如下:
$ sudo apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client # 这样安装的会是mysql 5.5左右
然后会看见输入密码的界面,你只需接下来输入管理员密码就行。
(2)修改 MySQL 的配置文件
$ sudo vim /etc/mysql/my.cnf
将 bind-address = 127.0.0.1 注释掉,就可以远程连接数据库了
https://github.com/rackerlabs/rackspace-how-to/edit/master/content/cloud-servers/installing-mysql-server-on-ubuntu.md
配置 mysql
https://github.com/rackerlabs/rackspace-how-to/edit/master/content/cloud-servers/configuring-mysql-server-on-ubuntu.md
mysql 开启远程连接
安装 mysql 后默认只支持 127.0.0.1 访问 3306 端口
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/mysql/conf.d$ netstat -aptn
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 10.1.1.236:22 10.1.1.232:50221 ESTABLISHED -
tcp 0 0 10.211.55.7:22 10.211.55.2:50237 ESTABLISHED -
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN -
要想让 mysql listen 0.0.0.0:3306 需要在其配置文件/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf找到bind-address = 127.0.0.1改成 bind-address = 0.0.0.0 这个操作需要管理员权限
然后重启 mysql
systemctl restart mysql
再次查看端口状态,发现已经在监听 0.0.0.0:3306 了
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d$ netstat -aptn
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
试下使用外网地址连接
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d$ mysql -h 10.211.55.7:3306 -u root -p
Enter password:
ERROR 2005 (HY000): Unknown MySQL server host '10.211.55.7:3306' (0)
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d$ mysql -h 10.211.55.7 -P 3306 -u root -p
Enter password:
ERROR 1130 (HY000): Host 'ubuntu.shared' is not allowed to connect to this MySQL server
发现失败了,第一个原因是不支持 host:3306 这样方式,需要用-h 10.211.55.7 -P 3306 这样的方式,第二个原因是 mysql 的 root 账户只开启了 localhost 访问权限,登录后使用SELECT host FROM mysql.user WHERE User = 'root';命令可查看
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d$ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 6
Server version: 5.7.23-0ubuntu0.16.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> SELECT host FROM mysql.user WHERE User = 'root';
+-----------+
| host |
+-----------+
| localhost |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
新建一个 mysql user 赋予远程访问权限
mysql> CREATE USER 'shiming'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'pass';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'shiming'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE USER 'shiming'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'pass';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'shiming'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
使用新建的用户登录,登录成功
ubuntu 下 terminal 复制/粘贴命令快捷键设置
Edit → Keyboard Shortcuts menu. 下可配置快捷键
ssh 配置免密码远程登陆
ssh-copy-id 将本地公钥 copy 到远程服务器允许的主机中去
$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@47.52.96.235
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/Users/Shiming/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '47.52.96.235 (127.0.0.1)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:H0LIGfcGjxFjilR+V6IQt/T97MGRczTQvmx2jXE3Irs.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@47.52.96.235's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@47.52.96.235'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
ssh 保持连接
ssh 远程连接服务器老是超时自动断开,如何保持不断?
方案一:在客户端设置
方法很简单,只需在客户端电脑上编辑(需要 root 权限)/etc/ssh/ssh_config,并添加如下一行:
ServerAliveInterval 30
此后该系统里的用户连接 SSH 时,每 30 秒会发一个 KeepAlive 请求,避免被踢。
方案二:在服务器设置
如果有相应的权限,也可以在服务器端设置,即编辑/etc/ssh/sshd_config,并添加:
ClientAliveInterval 60
重启 SSH 服务器后该项设置会生效。每一个连接到此服务器上的客户端都会受其影响。应注意启用该功能后,安全性会有一定下降(比如忘记登出时……)
mac 中命令行调用起 vscode 打开目录/文件
https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/setup/mac
开机启动服务
Ubuntu 开机之后会执行/etc/rc.local 文件中的脚本,可以直接在/etc/rc.local 中添加启动脚本, 要添加到语句:exit 0 前面才行。
sudo vi /etc/rc.local
rc.local 文件:
#!/bin/sh -e
#
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
# add by shiming to auto run in system restart for bitcoin testnet and ethereum testnet
nohup geth --testnet --datadir /mnt/ethereum/ --syncmode "full" --rpc --ws &
nohup btcd --testnet --datadir /mnt/bitcoin/ &
exit 0
使用 nginx 反向代理本地端口
nginx 的配置文件位置为 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
但是在这个配置中 include 了其他配置文件
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
所以我们在 conf.d 中编写配置文件即可 /etc/nginx/conf.d/btcd.conf
server{
listen 9000; # 对外端口
# using web1 sub domain to access
server_name 127.0.0.1 47.75.70.201;
access_log /var/log/nginx/btcd.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:18334; # 代理端口
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
配置完了检查 nginx 配置是否正确
$ conf.d nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
重启 nginx 生效配置
➜ conf.d systemctl restart nginx
查看端口是否被监听
➜ conf.d lsof -i:9000
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
nginx 2821 root 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2822 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2823 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2824 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2825 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2826 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2827 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2828 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
nginx 2830 www-data 7u IPv4 535089 0t0 TCP *:9000 (LISTEN)
在命令行中调用 sublime text 编辑文本
执行以下命令
ln -s "/Applications/Sublime Text.app/Contents/SharedSupport/bin/subl" /usr/local/bin/sublime
参考 https://olivierlacan.com/posts/launch-sublime-text-3-from-the-command-line/
隐藏身份
清除 Linux 的最近登录日志和 Bash 历史 http://topspeedsnail.com/clear-last-linux-login-log/
使用 tor 实现匿名扫描/SSH 登录 http://topspeedsnail.com/use-tor-hide-your-ass/
troubleshooting
字符编码问题
-bash: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directory
centos ssh 登录,登录成功但是报 -bash: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directory
➜ ~ ssh shiming@10.211.55.13
shiming@10.211.55.13's password:
Last login: Sat Oct 13 19:33:34 2018
-bash: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directory
[shiming@centos ~]$
解决方案:
sudo vi /etc/environment
然后加上这两行,再次登录就不会报了:
LANG=en_US.utf-8
LC_ALL=en_US.utf-8
ssh connection refused
- 先判断 ssh 是否安装
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ ps -e | grep ssh
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ /etc/init.d/ssh -start
bash: /etc/init.d/ssh: No such file or directory
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ whichis ssh
whichis: command not found
发现 ssh 未安装
- 安装 ssh-server
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
- 启动 ssh 服务
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ systemctl start sshd
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ ps -e|grep ssh
5602 ? 00:00:00 sshd
- 本地连接 ssh 进行测试
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ ssh shiming@localhost
The authenticity of host 'localhost (127.0.0.1)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:fHN3yPgM87SlGdXxzvvCGzqf3ARmN2iyyq9EfNwSMo4.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
shiming@localhost's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.10.0-28-generic x86_64)
- ifconfig 查看外网地址
inet 即外网地址
shiming@ubuntu:/etc/ssh$ ifconfig
enp0s5 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:1c:42:28:80:a2
inet addr:10.211.55.7 Bcast:10.211.55.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2598:3ddc:aea:479b/64 Scope:Link
inet6 addr: fdb2:2c26:f4e4:0:2cb3:821a:c4:a047/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fdb2:2c26:f4e4:0:2991:5c69:98eb:d6a5/64 Scope:Global
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1142 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:840 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1332342 (1.3 MB) TX bytes:83530 (83.5 KB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:310 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:310 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:27329 (27.3 KB) TX bytes:27329 (27.3 KB)
- 通过外网进行 ssh 连接(略)
vi 编辑,上下左右箭头变成 ABCD/delete 键无法删除解决办法
https://askubuntu.com/questions/353911/hitting-arrow-keys-adds-characters-in-vi-editor
关闭 ubuntu 图形界面
关闭图形界面可以让虚拟机少占用一些资源
参考: https://wiki.zthxxx.me/wiki/%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91/Linux/Ubuntu/Ubuntu-16-%E5%BC%80%E6%9C%BA%E9%BB%98%E8%AE%A4%E5%91%BD%E4%BB%A4%E8%A1%8C%E7%95%8C%E9%9D%A2/
shiming@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl set-default multi-user.target
[sudo] password for shiming:
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target.
关闭 centos 图形界面
➜ ~ systemctl set-default multi-user.target
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target.
显示当前主机的信息
$ hostnamectl
修改 hostname
hostnamectl set-hostname newhostnameyouwant
注意:/etc/hosts 文件中 127.0.0.1 映射的 hostname 要自己手动修改
将远程服务器的文件复制到本地剪贴板
ssh -e none root@47.75.70.201 "cat /tmp/bb.conf" | pbcopy #到本地剪贴板
pbpaste > /tmp/bb.txt #本地剪贴板到本地文件
升级 vim
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39861793/how-update-vim-to-8-0-version-in-osx
spacevim 字体问题
spacevim 使用的是 nerd 字体,系统一般都没有装,会导致图标乱码,虽然不影响使用,但是看到乱码很烦人
安装字体的步骤(mac 好装,有 brew 命令,以下是 linux 的安装步骤):
- 去 nerd 官网找到对应的系统 https://nerdfonts.com/,下载字体压缩文件,比如ubuntu
https://github.com/ryanoasis/nerd-fonts/releases/download/v2.0.0/Ubuntu.zip - 在 linux 中解压字体包,得到.ttf 的字体文件
- 将字体文件复制到
/usr/share/founts目录或者/usr/local/share/fonts目录,如果目录不存在就新建
man: can’t set the locale; make sure $LC_* and $LANG are correct
问题原因: Mac OS X ssh 登陆 Linux 是终端提示 cannot change locale
man命令运行后一直出这个提示,字符集问题,先运行:
sudo locale-gen "en_US.UTF-8"
sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
然后在/etc/default/locale加入以下行
LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"
reference
bash reference
http://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/bashref.html
 刘世明的博客
刘世明的博客






最新评论